Overview
Key Features
-
🧠 Semantic Understanding of Queries
Utilizes sentence embeddings and transformer-based language models to interpret user intent beyond keywords. -
⚖️ Contextual Retrieval of IPC Sections
Retrieves the most relevant sections and clauses of the Indian Penal Code using vector similarity search (cosine similarity) instead of plain text lookup. -
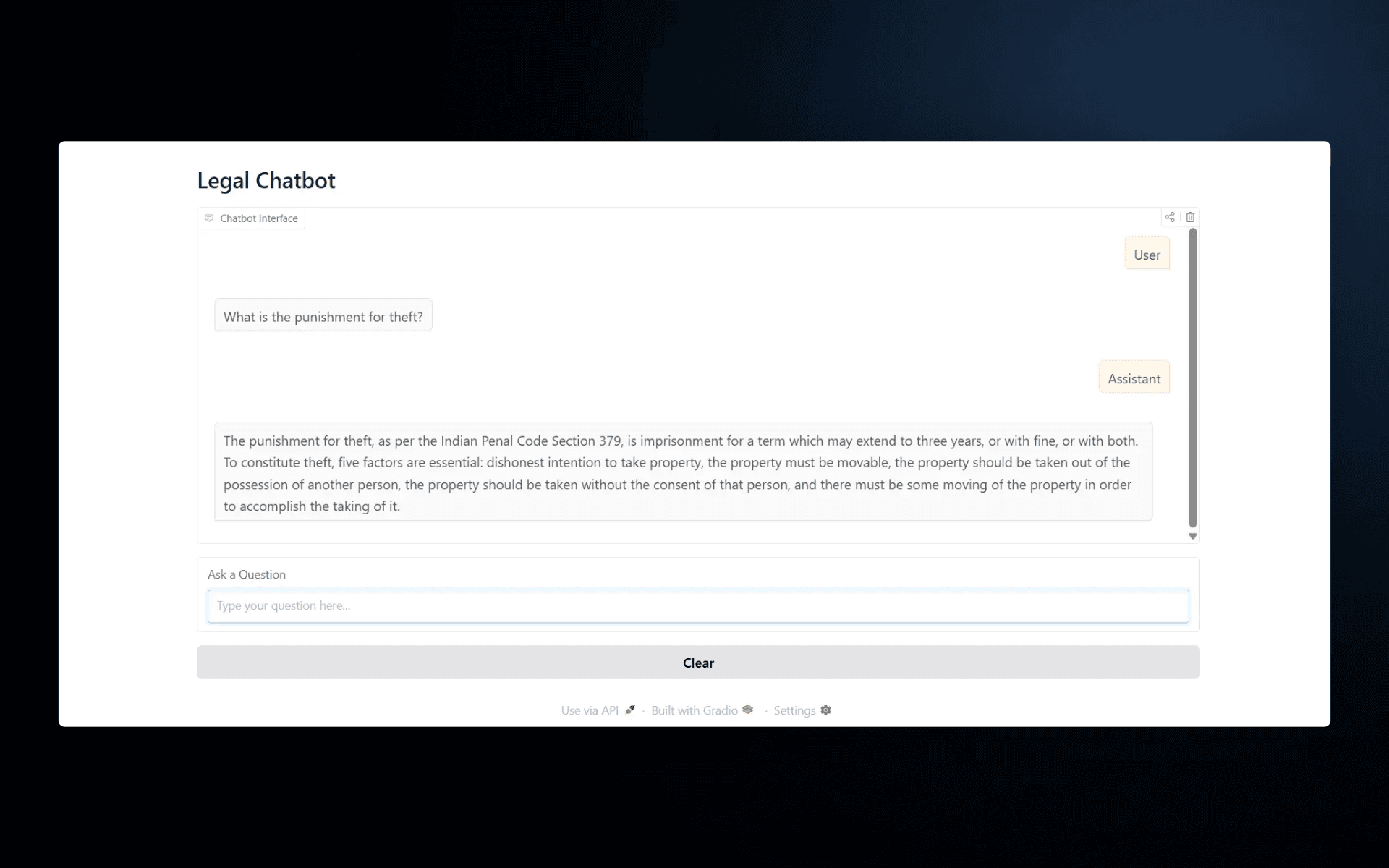
💬 Interactive Gradio Interface
A clean, conversational UI built with Gradio for seamless question–answer interactions and real-time feedback. -
📚 Structured Legal Dataset
Preprocessed IPC dataset containing section numbers, descriptions, and legal explanations for fast semantic search. -
🔍 Intelligent Response Generation
Combines retrieved legal text with summarization logic to generate clear, simplified explanations for users. -
📈 Scalable and Extensible Design
Can easily be extended to cover additional acts (like CrPC, IT Act, etc.) or connected to external databases and legal APIs.
Technologies Used
- Frontend: Gradio (Python Web UI)
- Backend / NLP: Python, Sentence-Transformers (e.g., nomic-ai/nomic-embed-text-v1), FAISS
- Data Source: Structured Indian Penal Code dataset (.pdf)
- Semantic Search: Cosine Similarity on Embedding Vectors
- Models : Hugging Face Transformers (mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2)
- Deployment: Hugging Face Spaces
Architecture Overview
- Parsed and structured IPC sections into a pickle file.
- Generated embeddings for all IPC clauses using a transformer model.
- When a user submits a query, it is embedded using the same model.
- The system computes semantic similarity between the query embedding and all IPC embeddings.
- The top-matching sections are retrieved and ranked by relevance score.
- Synthesizes a clear, concise explanation combining the retrieved section and relevant context.
- Returns the answer through the Gradio interface with a link to the IPC section reference.
- Gradio app handles user inputs, displays responses, and enables conversational flow.
Challenges and Learnings
-
Legal Language Complexity:
Handling formal and archaic legal wording required extensive preprocessing, including lemmatization and abbreviation normalization. -
Semantic Ambiguity:
Many legal queries overlap conceptually (e.g., theft vs. robbery). Implementing cosine similarity thresholding helped improve precision. -
Model Performance:
Experimented with different transformer models for optimal balance between accuracy and latency for real-time responses. -
Explainability:
Ensured responses included section references and source text to maintain trust and transparency.
Outcome
- Successfully developed a legal chatbot that delivers accurate, understandable, and reference-backed answers to legal questions.
- Demonstrated how semantic search and NLP can make complex domains like law accessible and conversational.
- Achieved high user satisfaction in tests with law students and paralegals who found it faster and more intuitive than manual lookup.
Conclusion
It reflects strong skills in retrieval-based NLP systems, knowledge graph construction, and AI-driven user interaction design, making it a valuable asset in both AI and legal-tech domains.